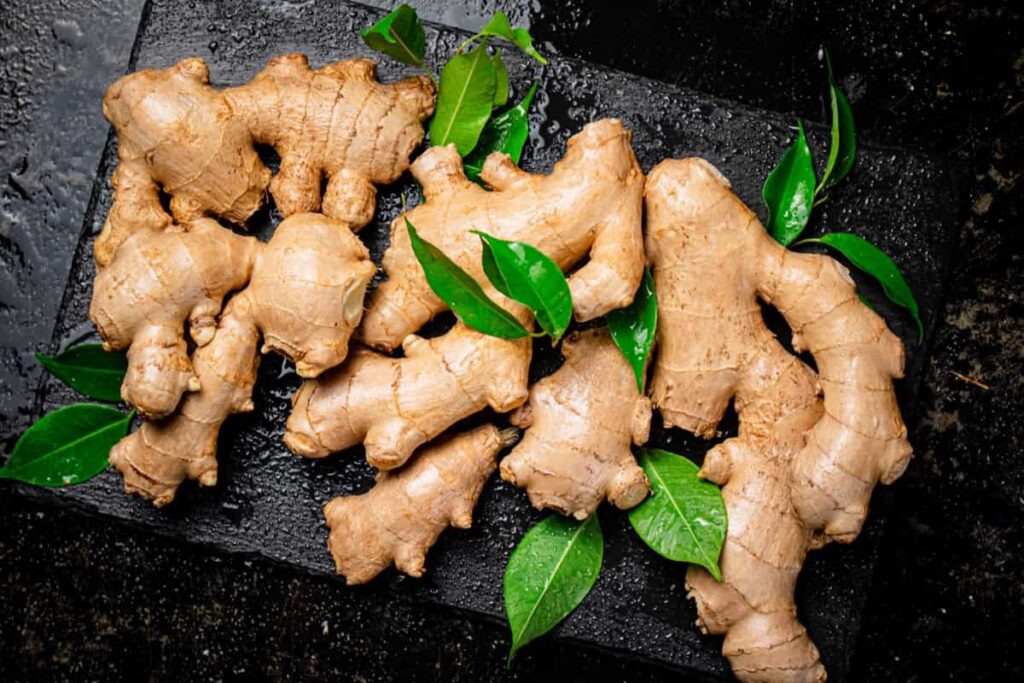
Ginger is one of the healthiest vegetables in the world and is also a very good natural remedy.
Ginger is filled with antioxidants, a substance that helps with cell damage, and gingerol. This is what makes ginger so healthy and why ginger is best for inflammation, nausea, digestion and heartburn.
1. Fights Inflammation and Provides Pain Relief
Ginger is loaded with anti-inflammatory compounds called gingerols and shogaols. These bioactive substances hold back the production of inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, in other words they reduce inflammation in the body. Because of this we recommend it for those with joint pain. Many individuals say that eating ginger in some shape or form has been shown to alleviate pain and improve mobility in individuals.
2. Aids Digestion and Relieves Nausea
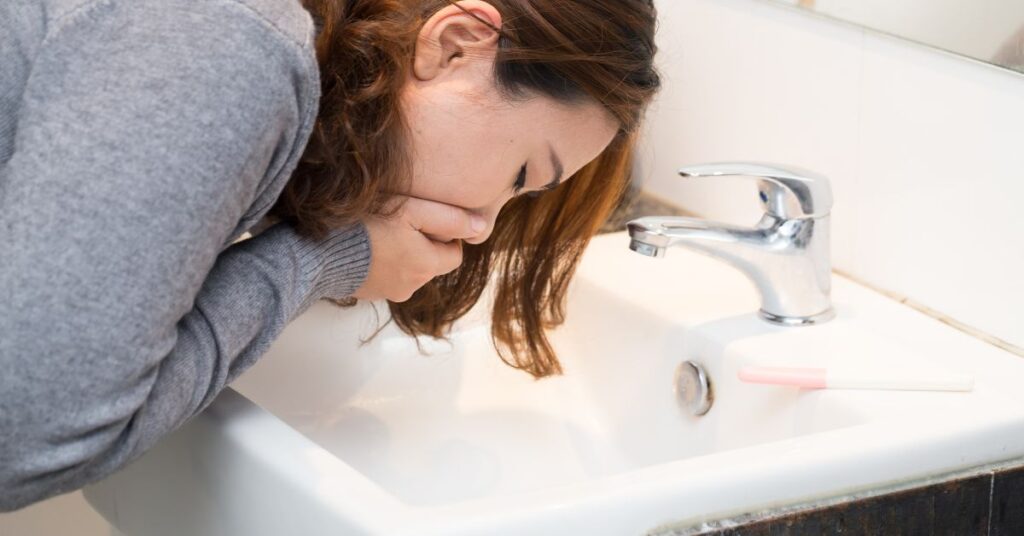

Ginger has a long history of use in alleviating digestive discomfort. It stimulates the production of saliva and bile, which helps in digestion therefore relieves nausea. Ginger is also effective in reducing nausea and vomiting, making it beneficial for:
• Pregnancy-Related Nausea: Studies have shown that ginger can safely reduce morning sickness symptoms in pregnant women.
• Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea: Ginger may help alleviate nausea in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, though more research is needed.
• Motion Sickness: Ginger has been found to be effective in reducing symptoms of motion-induced nausea.
3. Boosts the Immune System
Ginger’s antioxidant properties help combat oxidative stress; this can and will weaken the immune system. By neutralizing free radicals, ginger supports the body’s defense mechanisms, reducing the risk of infections. Additionally, ginger has antimicrobial properties that help fight off pathogens.
4. Supports Heart Health
Regular consumption of ginger has been linked to various cardiovascular benefits:
• Lowers Blood Pressure: Ginger acts as a vasodilator, expanding blood vessels and improving blood flow, which can help reduce blood pressure.
• Reduces Cholesterol Levels: Studies suggest that ginger can lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease.
• Prevents Blood Clotting: Ginger has antiplatelet properties, which may help prevent the formation of blood clots, reducing the risk of stroke and heart attacks.
5. Aids in Weight Loss
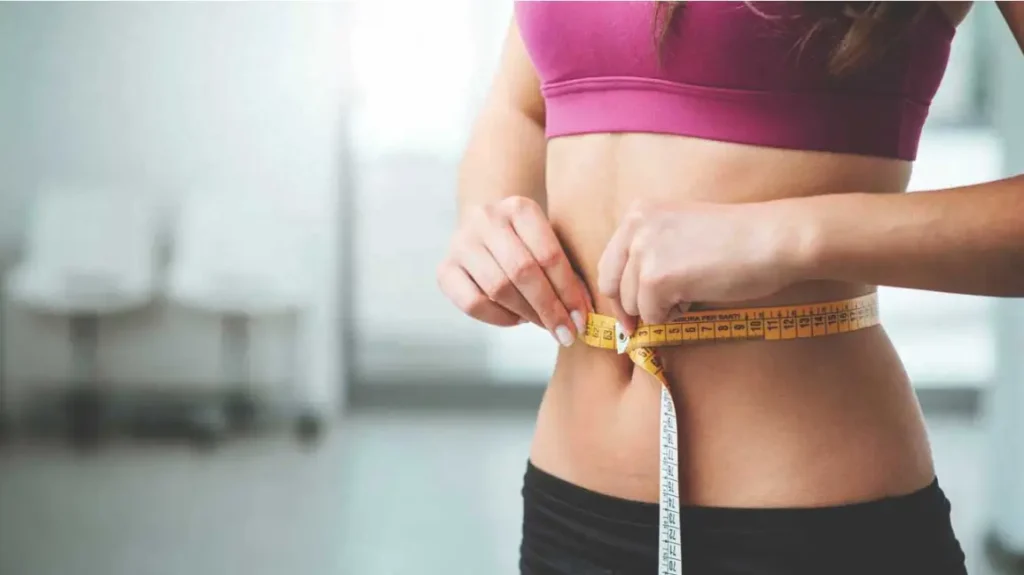

Ginger may contribute to weight management through several mechanisms:
• Enhances Thermogenesis: Ginger increases the body’s metabolic rate, leading to greater calorie burn.
• Suppresses Appetite: Consuming ginger can promote feelings of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake.
• Improves Fat Metabolism: Ginger has been shown to enhance the breakdown of fats for energy.
These effects collectively support weight loss efforts when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
6. Improves Brain Function
Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation are key contributors to age-related cognitive decline. The antioxidants and bioactive compounds in ginger can inhibit inflammatory responses in the brain. Some studies suggest that ginger can enhance cognitive functions, including attention and memory.
7. Lowers Blood Sugar Levels
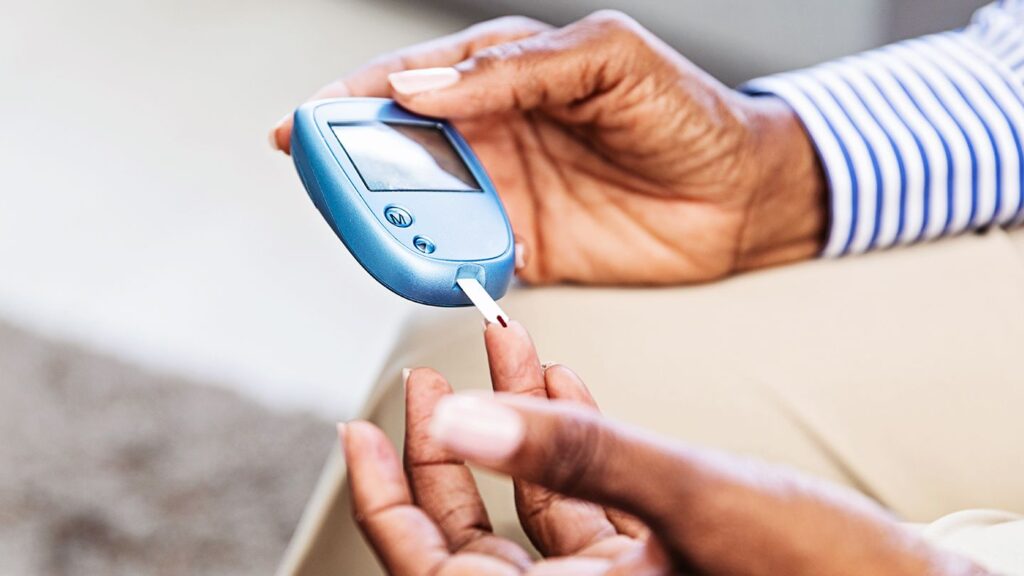
Ginger has been studied for its potential antidiabetic properties:
• Enhances Insulin Sensitivity: Ginger may improve the body’s responsiveness to insulin, facilitating better blood sugar control.
• Lowers Fasting Blood Sugar: Regular intake of ginger has been associated with reductions in fasting blood glucose levels.
These effects can be beneficial for individuals managing type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
8. Reduces Migraine
Ginger’s anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties help alleviate migraine symptoms. It is believed to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins, which play a role in pain and inflammation. Some studies have found that taking ginger at the onset of a migraine can reduce its severity and duration.
9. Supports Oral Health
The antimicrobial properties of ginger contribute to oral health by inhibiting the growth of pathogens in the mouth. This can help prevent infections, reduce inflammation, and promote overall oral hygiene.
10. Eases Respiratory Discomfort
Ginger’s anti-inflammatory properties can help alleviate respiratory issues, such as coughs and colds. Its warming effect can help break down mucus, making it easier to expel and relieving congestion.
11. Enhances Skin Health
The antioxidants in ginger can promote healthier skin by combating oxidative stress, potentially reducing signs of aging and improving skin elasticity. Additionally, ginger’s anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce skin irritation and redness.
12. Combats Oxidative Stress
Ginger’s antioxidant properties help neutralize free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases. This protective effect supports overall health and longevity.
Incorporating ginger into your diet can be a flavorful and natural way to support various aspects of health. However, it’s important to consume it in moderation and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
.
How to Use Ginger
Ginger is versatile and can be enjoyed in many forms:
• Fresh or Dried: Add to stir-fries, soups, or salads.
• Powdered: Use in baking or sprinkle over your favorite dishes.
• Tea: Brew fresh ginger slices in hot water for a soothing drink.
• Supplements: Available in capsule or extract form if you need a more concentrated dose.
While ginger is natural and generally safe, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before using it as a remedy. Especially if you are pregnant, taking medication, or have a chronic health condition.
